Understanding STEM and STEAM Education
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the demand for skills in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) continues to grow. STEM education aims to equip students with the knowledge and skills necessary to tackle complex problems, innovate, and thrive in a technology-driven society. However, in recent years, there has been a push to incorporate the arts into STEM education, giving rise to the STEAM movement.
STEM: A Focus on Core Disciplines
STEM education focuses on four core disciplines: science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It emphasizes hands-on learning, critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration. STEM programs often involve activities such as conducting experiments, coding, building robots, and designing solutions to real-world problems. By mastering STEM concepts and skills, students gain a solid foundation in areas like scientific inquiry, computer science, and mathematical reasoning.
The Rise of STEAM: Integrating the Arts
STEAM education builds upon the foundation of STEM by adding the arts into the mix. The “A” in STEAM represents disciplines such as visual arts, music, theater, and design. By integrating the arts into STEM education, STEAM programs aim to foster creativity, innovation, and interdisciplinary thinking. Students engage in activities that blend scientific inquiry with artistic expression, allowing them to explore connections between different disciplines and approach challenges from multiple perspectives.
Benefits of STEAM Education
One of the key benefits of STEAM education is its ability to cultivate creativity and innovation. By encouraging students to think creatively and express themselves artistically, STEAM programs help develop the essential skills needed for success in the 21st century. Additionally, STEAM education promotes collaboration, communication, and problem-solving skills, as students work together to tackle complex projects and explore new ideas.
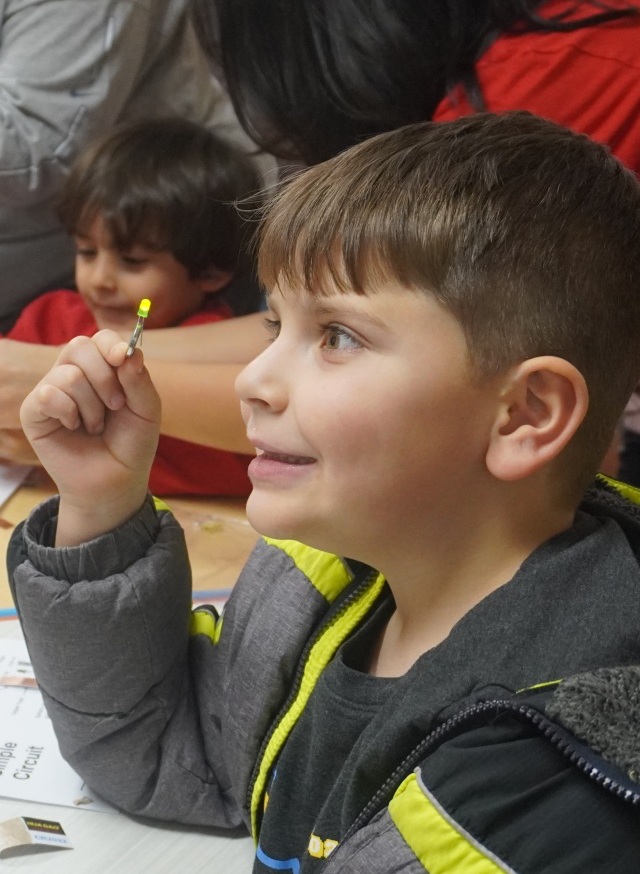

STEAM in Action: An Interdisciplinary Approach
In a STEAM classroom, students might explore topics such as environmental science through photography, engineering through sculpture, or mathematics through music. For example, students could design and build a model bridge to learn about structural engineering principles while incorporating elements of art and design into their final product. By engaging in hands-on, project-based learning experiences, students develop a deeper understanding of STEM concepts while honing their artistic skills and creativity.
Choosing Between STEM and STEAM
While STEM provides a solid foundation in core disciplines and technical skills, STEAM offers a more holistic approach that integrates creativity, innovation, and artistic expression. Ultimately, both STEM and STEAM education play valuable roles in preparing students for success in a rapidly changing world.
Conclusion: Embracing Innovation and Creativity
In conclusion, STEM and STEAM education are both valuable approaches to learning that offer unique benefits to students. While STEM focuses on core disciplines and technical skills, STEAM integrates the arts to foster creativity, innovation, and interdisciplinary thinking. By embracing both STEM and STEAM principles, educators can provide students with a well-rounded education that prepares them for the challenges and opportunities of the future.
